India Government set a milestone in the history of the Indian education system by replacing the 34-year-old NEP framed in 1986 by NEP-2020, approved by Union Cabinet. We will discuss the key points and highlights of NEP-2020
- The NEP 2020 will help to make “India a Global Knowledge superpower”
- NEP-2020 is the third major revamp of the framework of education since Independence.
- The cabinet has approved the renaming of the Ministry of Human Resource Development to the Ministry of Education.
New Education Policy Highlights
School Education
- Universalization of education from preschool to secondary level with 100% gross enrollment Ration (GER) in school education by 2020
- NEP 2020 will bring two crores out of school children back into the mainstream
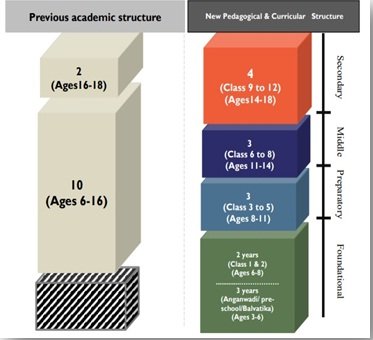
- The NEP expands the age group of 6-14 years of mandatory schooling to 3-18 years of schooling from 3-18 years of schooling. They uncovered a 3-6 year age group also included under the school curriculum. The system will have 12 years of schooling with 3 years of Anganwadi/ pre-schooling.
- With an emphasis on early childhood care and Education(ECCE), the 10+2 structure of the school curriculum is to be replaced by a 5+3+3+4 curriculum structure corresponding to ages 3-8, 8-11, 11-14, and 14-18 years respectively.
- NEP puts focus on a student’s mother tongue as the medium of instruction( not compulsory).
- Vocational Education starts from class 6 with an internship. They will learn coding from class 6.
- According to NEP 2020, There will be no rigid separations between arts and science, between curriculum and extra-curriculum activities, between vocational and academic streams. Students can choose subjects as per their choice.
- Class 10 and 12 exams will be made easier and the aim of the assessment of our schooling system will shift from summative and primary tests rote memorization skills to test the skills such as analysis, critical thinking, and conceptual clarity.
- Assessment reforms with 360-degree Holistic progress card, tracking student progress for achieving learning outcome, etc.
- By 2030, the minimum degree qualification for teaching will be a 4-year integrated B.Ed. degree
Higher Education
- Higher Education Commission of India (HECI) will be set up as a single umbrella body for the entire higher education, excluding medical and legal education
- Public and private higher education institutions will be governed by the same set of norms for regulation, accreditation, and academic standards. Also, HECI will be having four independent verticals namely,
- National Higher Education Regulatory Council (NHERC) function for regulation
- General Education Council (GEC) function for standard-setting
- Higher Education Grants Council (HEGC) function for funding
- National Accreditation Council (NAC) functions for accreditation.
- Govt. will phase out the affiliation of colleges in 15 years and a stage-wise mechanism is to be established for granting graded autonomy to colleges.
- The undergraduate degree will be of either 3 or 4 years duration with multiple exit options. The college will be mandated to give certification after completing the 1-year course, a diploma after 2 years of study, a bachelor’s after a 3-year program, bachelor’s research degree after 4 years of study.
- M.Phil. courses will be discontinued and all courses at undergraduate, postgraduate, and Ph.D. levels will now be interdisciplinary.
- National Assessment centre-PARAKH has been created to access the students
- Foreign universities can setup campus India.
- 6% of GDP will be invested in the Education sector.
- The National Scholarship Portal will be expanded to track the progress of students receiving scholarships.
- The policy aims to achieve 100% of youth and adult literacy.
New Education Policy Advantages
We can see the Advantages in every statement of this policy. but the NEP-2020 will bring a revolutionary change in India if the policy will be implemented successfully.

